
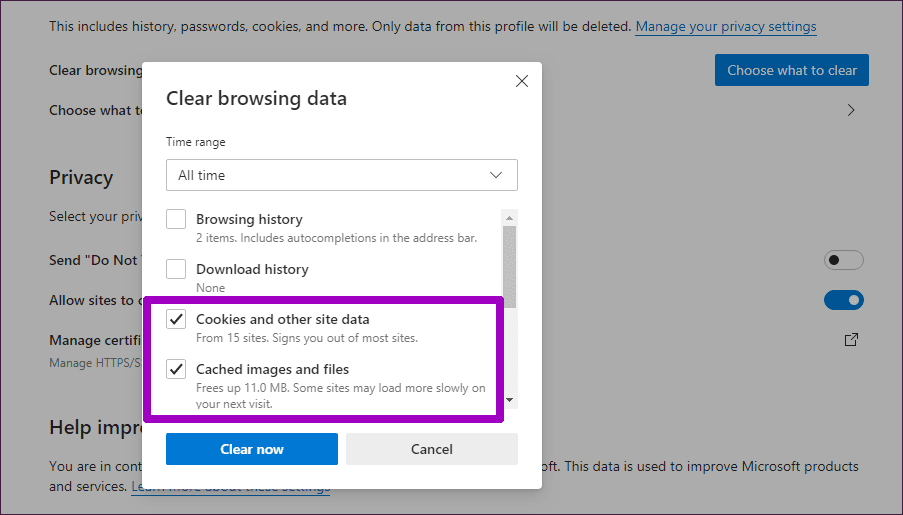
If you browse the Internet on your phone, you may notice that bandwidth limits and caps can disrupt your online experiences. If you do a lot of online shopping, a cache can improve your experience because consistent information like logos and buttons will load quickly, since they typically appear in the same place on every product page. By keeping some of that information in a cache for future use, when you visit that page again, it will load much more quickly, speeding up web browsing. You may notice that when you visit a website for the first time, it may load slowly, based on how much code your computer or smart device must download.
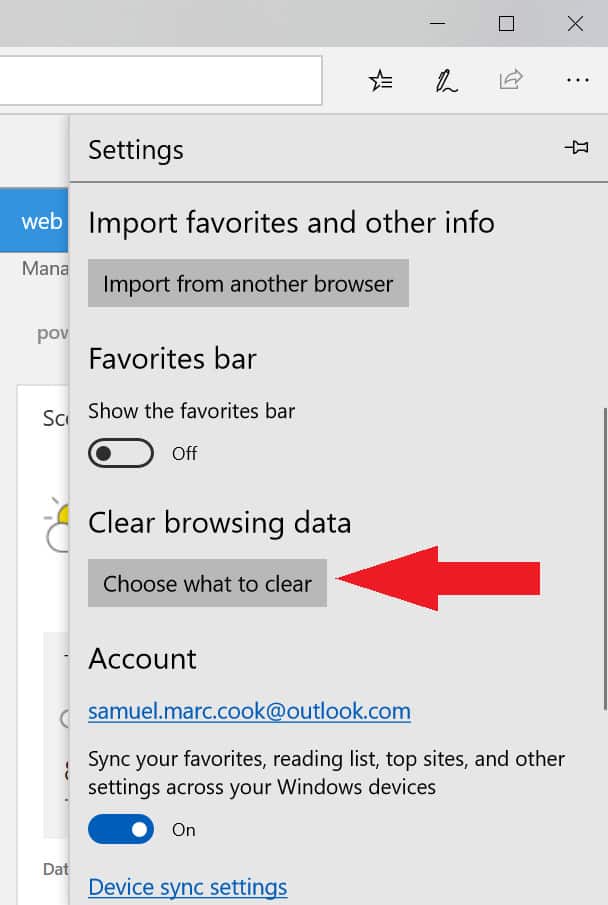
A browser cache functions in the same way. Think of how you can typically recall a song’s lyrics if you hear it again for the first time in months. The cache is stored on your smart phone, tablet, or computer’s hard drive and helps websites load faster because some of the page’s information already lives in your device. Typically, a browser will store what are known as static assets, parts of a website that don’t frequently change.
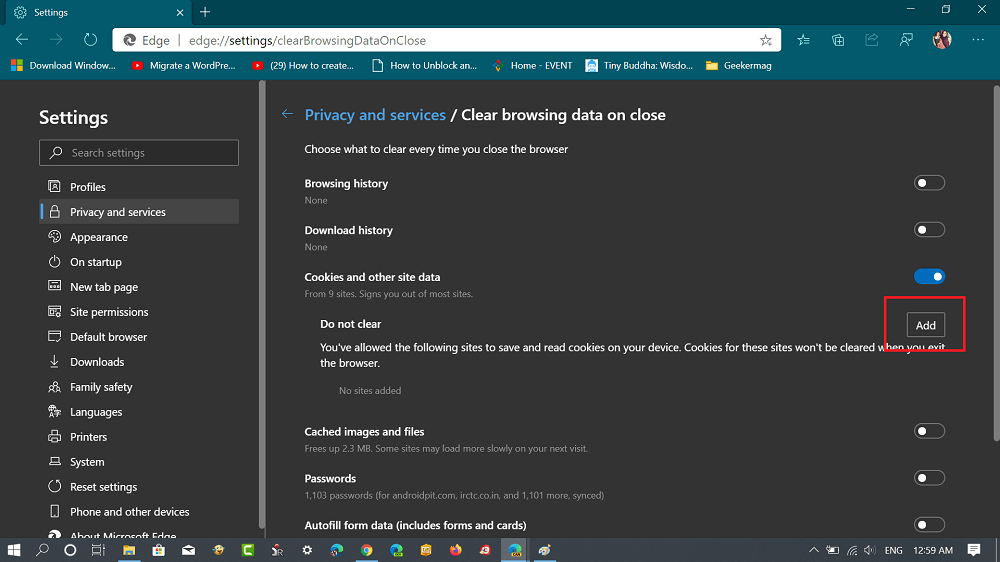
This information could include the text from the site or some of the images like logos, backgrounds. When you visit a website, your browser downloads certain information from that site to help it load faster when you revisit it in the future.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
